
The slide is flushed with an Iodine solution, which fixes the Crystal Violet to the cell wall, followed by a decolorizer (an alcohol) to wash away any non-fixed Crystal Violet. The heat-fixed sample is stained with Crystal Violet, turning the cells purple. Briefly, a bacterial smear is placed on a microscope slide and then heat-fixed to adhere the cells to the slide and make them more readily accepting of stains (1). The Gram stain, developed in 1884 by the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram (1), differentiates bacteria based on the composition of the cell wall (1, 2, 3, 4).
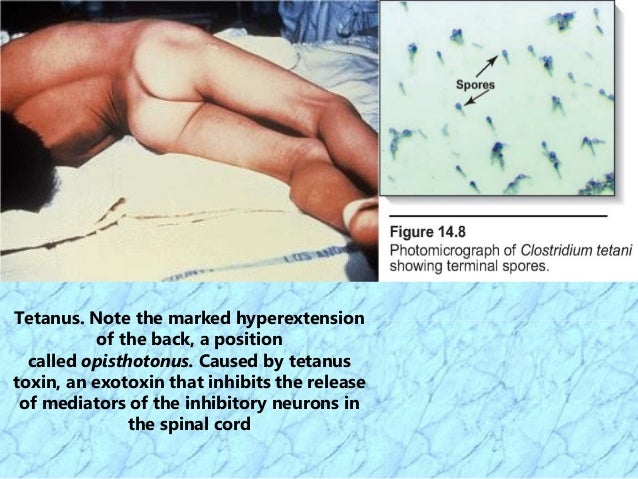
The most important parts of the microscope are labeled. Here, we will discuss visualizing bacteria with Gram stains, Capsule stains, and Endospore stains.įigure 1: A typical compound microscope. Typically, compound microscopes have multiple objective lenses of varying powers to allow for different magnification (1, 2). Combining the objective lens and eyepiece allows for higher magnification than using a single lens alone. This is then magnified by the eyepiece (ocular lens) which enlarges the image. Compound microscopes have an objective lens close to the object which collects light to create an image of the object. Simple microscopes (for example a magnifying glass) have only one lens to magnify an object, while compound microscopes have several lenses to enhance magnification (Figure 1). The main difference between them is the number of lenses used to magnify the object. The two main types of light microscopes are simple and compound. Staining bacteria is necessary when distinguishing bacterial types with light microscopy. To observe these properties, one can use light microscopy however, some bacterial characteristics (for example size, lack of coloration, and refractive properties) make it hard to distinguish bacteria solely with a light microscope (1, 2). Many properties help distinguish them from each other, including but not limited to Gram-staining type, shape and arrangement, production of capsule, and formation of spores. DiRita 1ġ Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan, United States of Americaīacteria are diverse microorganisms found nearly everywhere on Earth. When favourable conditions arrive, spores reactivate into new bacteria.Source: Rhiannon M. Spore coat is formed by the formation of peptidoglycan layer between 2 layers. Calcium dipicolinate is present in Forespore. It leaves a double membrane around the DNA. Forespore is formed by pinching the membrane into the cell. DNA replicates and septum form between genetic material and the rest of the cell. A membrane between the DNA and cortex is present that is called as septum. When favourable conditions arrive, spores germinate into bacteria which is called sporulation. Some spores are present sub-terminally that are present between the two extremes of the cell.Terminal spores are those that are present in the terminal of the cell.Some spores are present in the centre of the cell.Calcium dipicolinate is present in high concentration that stabilizes the DNA molecule present in spore.ĭipicolinaic acid helps the spore to resist the heat fluctuations in the environment and calcium helps the spore from oxidizing agents. They also contain ribosomes and enzymes that are metabolically inactive. SASPs help in the protection of the DNA from UV radiation and heat. The core contains the bacterial DNA that is enclosed into Small acid-soluble spore protein (SASPs). Peptidoglycan is needed for the synthesis of the cell wall. Cortex:Ĭortex lies beneath the coat and it mainly composed of peptidoglycan. It is composed of keratin that has the enzymes that allow the germination of spore. It excludes large molecules such as lysozyme and toxins from the spore.

It is a thin covering around the spore that acts as a sieve. Resistance to temperature and pH change.depletion of nutrient, high in temperature and pH and dehydration, bacteria forms spores. The bacteria that germinate from spore can grow and start a new progeny.Ĭlostridium botulinum, Bacillus anthracis Why bacteria produce spores?īacteria grow moderately in favourable condition. When favourable conditions arrive, these spores germinate into a new bacterium that has all the properties of the parent bacteria. Spores have the least metabolic activity. Spores are the dormant form of bacteria that can tolerate all the fluctuations in the environment. Spore-forming bacteria are those bacteria that can form spores under unfavourable conditions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
